TriviaQA: A Large Scale Distantly Supervised Challenge Dataset for Reading Comprehension
@article{Joshi2017TriviaQAAL,
title={TriviaQA: A Large Scale Distantly Supervised Challenge Dataset for Reading Comprehension},
author={Mandar Joshi and Eunsol Choi and Daniel S. Weld and Luke Zettlemoyer},
journal={ArXiv},
year={2017},
volume={abs/1705.03551},
url={https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:26501419}
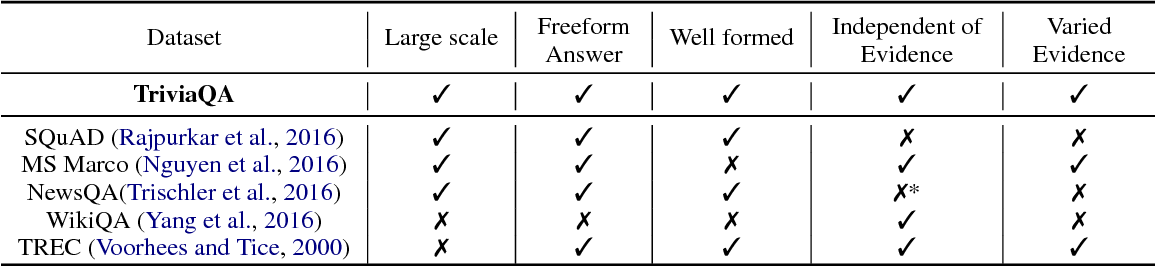
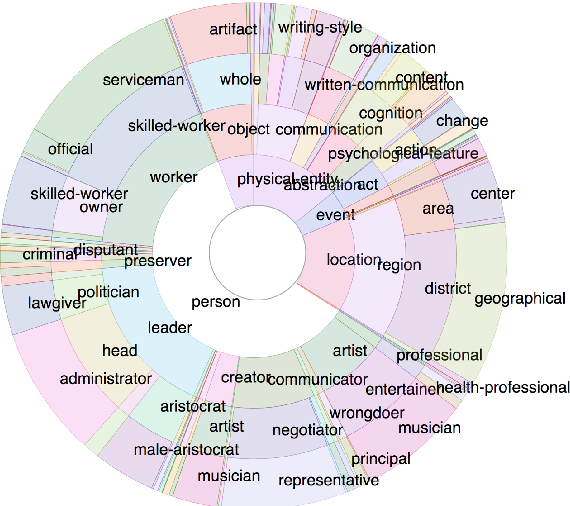
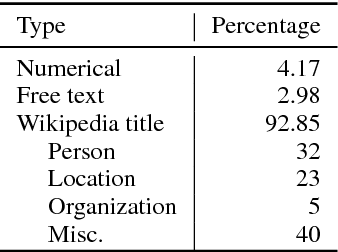
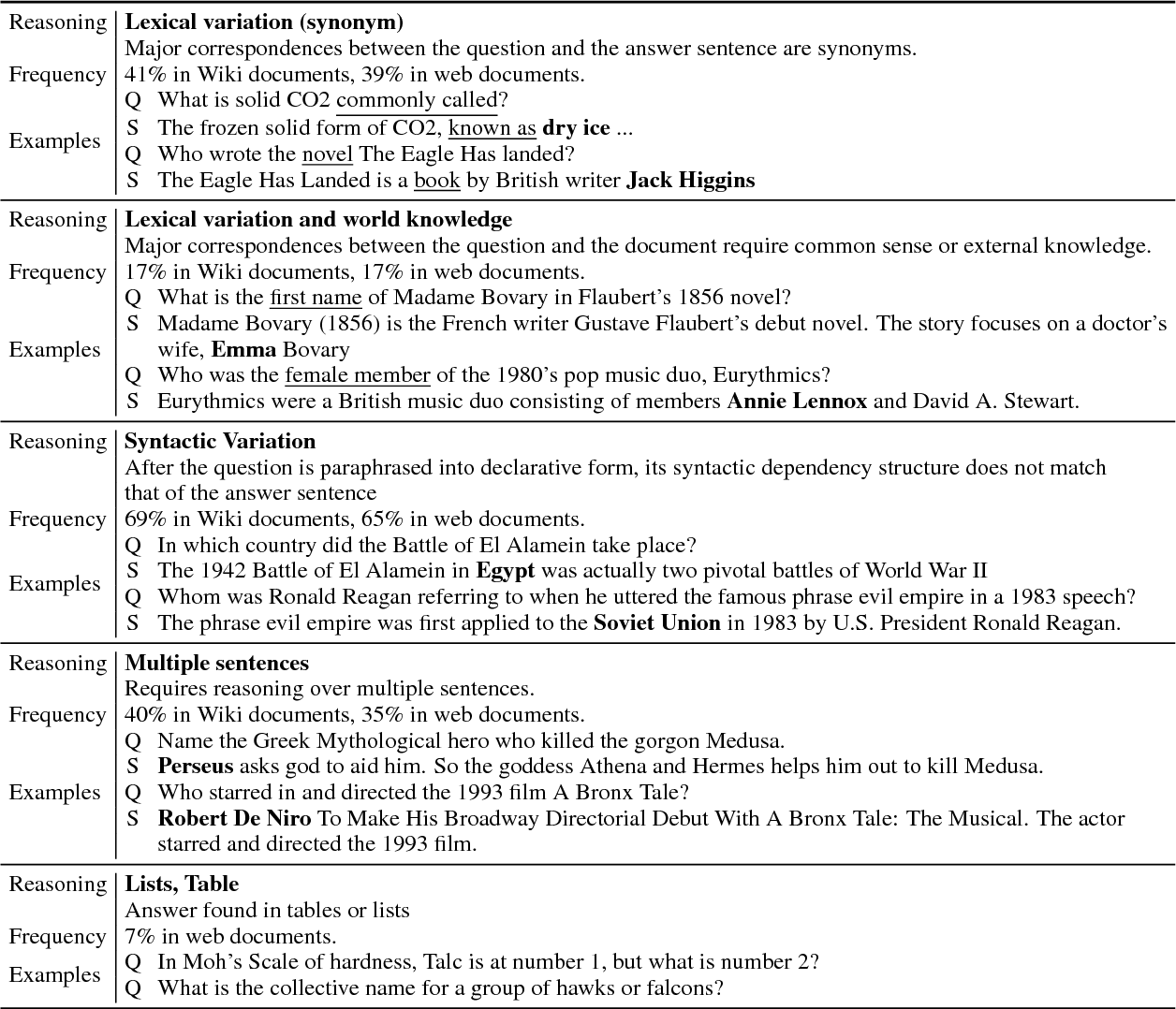
}It is shown that, in comparison to other recently introduced large-scale datasets, TriviaQA has relatively complex, compositional questions, has considerable syntactic and lexical variability between questions and corresponding answer-evidence sentences, and requires more cross sentence reasoning to find answers.
Topics
TriviaQA (opens in a new tab)Trivia Enthusiasts (opens in a new tab)Reading Comprehension (opens in a new tab)TriviaQA Dataset (opens in a new tab)Evidence Documents (opens in a new tab)NewsQA (opens in a new tab)Bidirectional Attention Flow (opens in a new tab)SearchQA (opens in a new tab)Cloze-style Datasets (opens in a new tab)Multi-sentence Reasoning (opens in a new tab)
3,211 Citations
Looking Beyond the Surface: A Challenge Set for Reading Comprehension over Multiple Sentences
- 2018
Computer Science, Education
The dataset is the first to study multi-sentence inference at scale, with an open-ended set of question types that requires reasoning skills, and finds human solvers to achieve an F1-score of 88.1%.
NLQuAD: A Non-Factoid Long Question Answering Data Set
- 2021
Computer Science
NLQuAD’s samples exceed the input limitation of most pre-trained Transformer-based models, encouraging future research on long sequence language models and shows that Longformer outperforms the other architectures, but results are still far behind a human upper bound.
R3: Reinforced Reader-Ranker for Open-Domain Question Answering
- 2017
Computer Science
A new pipeline for open-domain QA with a Ranker component, which learns to rank retrieved passages in terms of likelihood of generating the ground-truth answer to a given question, and a novel method that jointly trains the Ranker along with an answer-generation Reader model, based on reinforcement learning.
R3: Reinforced Ranker-Reader for Open-Domain Question Answering
- 2018
Computer Science
This paper proposes a new pipeline for open-domain QA with a Ranker component, which learns to rank retrieved passages in terms of likelihood of extracting the ground-truth answer to a given question, and proposes a novel method that jointly trains the Ranker along with an answer-extraction Reader model, based on reinforcement learning
MKQA: A Linguistically Diverse Benchmark for Multilingual Open Domain Question Answering
- 2021
Linguistics, Computer Science
Multilingual Knowledge Questions and Answers is introduced, an open- domain question answering evaluation set comprising 10k question-answer pairs aligned across 26 typologically diverse languages, making results comparable across languages and independent of language-specific passages.
A Framework for Evaluating MRC Approaches with Unanswerable Questions
- 2022
Computer Science
A data augmentation approach is proposed that converts answerable questions to unanswerable questions in the SQuAD 2.0 dataset by altering the entities in the question to its antonym from ConceptNet which is a semantic network.
Translucent Answer Predictions in Multi-Hop Reading Comprehension
- 2020
Computer Science
This paper proposes a novel deep neural architecture, called TAP (Translucent Answer Prediction), to identify answers and evidence (in the form of supporting facts) in an RCQA task requiring multi-hop reasoning.
Quizbowl: The Case for Incremental Question Answering
- 2019
Computer Science
This work makes two key contributions to machine learning research through Quizbowl: collecting and curating a large factoid QA dataset and an accompanying gameplay dataset, and developing a computational approach to playing Quiz Bowl that involves determining both what to answer and when to answer.
Getting Closer to AI Complete Question Answering: A Set of Prerequisite Real Tasks
- 2020
Computer Science
QuAIL is presented, the first RC dataset to combine text-based, world knowledge and unanswerable questions, and to provide question type annotation that would enable diagnostics of the reasoning strategies by a given QA system.
Relation Module for Non-Answerable Predictions on Reading Comprehension
- 2019
Computer Science
This paper aims to improve a MRC model’s ability to determine whether a question has an answer in a given context (e.g. the recently proposed SQuAD 2.0 task), and shows the effectiveness of the relation module on MRC.
38 References
SQuAD: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text
- 2016
Computer Science
A strong logistic regression model is built, which achieves an F1 score of 51.0%, a significant improvement over a simple baseline (20%).
NewsQA: A Machine Comprehension Dataset
- 2017
Computer Science
NewsQA, a challenging machine comprehension dataset of over 100,000 human-generated question-answer pairs, is presented and analysis confirms that NewsQA demands abilities beyond simple word matching and recognizing textual entailment.
MS MARCO: A Human Generated MAchine Reading COmprehension Dataset
- 2016
Computer Science
The size of the dataset and the fact that the questions are derived from real user search queries distinguishes MS MARCO from other well-known publicly available datasets for machine reading comprehension and question-answering.
A Thorough Examination of the CNN/Daily Mail Reading Comprehension Task
- 2016
Computer Science
A thorough examination of this new reading comprehension task by creating over a million training examples by pairing CNN and Daily Mail news articles with their summarized bullet points, and showing that a neural network can be trained to give good performance on this task.
Large-scale Simple Question Answering with Memory Networks
- 2015
Computer Science
This paper studies the impact of multitask and transfer learning for simple question answering; a setting for which the reasoning required to answer is quite easy, as long as one can retrieve the correct evidence given a question, which can be difficult in large-scale conditions.
Dataset and Neural Recurrent Sequence Labeling Model for Open-Domain Factoid Question Answering
- 2016
Computer Science
This work casts neural QA as a sequence labeling problem and proposes an end-to-end sequence labeling model, which overcomes all the above challenges and outperforms the baselines significantly on WebQA.
MCTest: A Challenge Dataset for the Open-Domain Machine Comprehension of Text
- 2013
Computer Science, Linguistics
MCTest is presented, a freely available set of stories and associated questions intended for research on the machine comprehension of text that requires machines to answer multiple-choice reading comprehension questions about fictional stories, directly tackling the high-level goal of open-domain machine comprehension.
Machine Comprehension
- 2018
Computer Science
This project implemented Match-LSTM model using answer pointer using boundary model and another model based on Scaled-Dot Product Attention and Multi-Head Attention, which gives better results.
SearchQA: A New Q&A Dataset Augmented with Context from a Search Engine
- 2017
Computer Science
It is shown that there is a meaningful gap between the human and machine performances, which suggests that the proposed dataset could well serve as a benchmark for question-answering.
MS MARCO: A Human Generated MAchine Reading COmprehension Dataset
- 2016
Computer Science
This new dataset is aimed to overcome a number of well-known weaknesses of previous publicly available datasets for the same task of reading comprehension and question answering, and is the most comprehensive real-world dataset of its kind in both quantity and quality.